Reverse SEO – What Is It And How Do You Do It?
What is Reverse SEO?
What exactly is reverse SEO? Not to be confused with negative SEO, reverse SEO is used for search engine reputation management (online reputation management).
Reverse search engine optimization is used to suppress or push down a web page in the search engine results. With reverse SEO, you are essentially burying search results that could be harmful to your brand or reputation.
When your brand’s reputation is at stake
They say that any press is good press. This is one of those classic business myths. Sure this may be true in some cases, but in the majority of cases, it can do some real damage to your brand’s image and sales.
You never know when something is going to happen that can affect your brand’s reputation. You may have an irate employee, a faulty product, or your company may make a mistake.
You may get some other websites talking about your company, other forums, and the press. Then, negative content about your company may start ranking on page one, when people search for your brand.
How reverse SEO works
Let’s say there is some negative press about your company ranking on page one when people search your brand. What do you do?
Well, you can boost other pages with SEO to effectively push that result down to page 2, where not many people will see it. Most people only look at results on page 1 unless they are doing more extensive research.
So, Reverse SEO is used to “push down” certain search results on the first page of Google, where they will be seen.
Real world example of Reverse SEO
United Airlines has had some bad press recently, and as a result, you may see some bad press when searching their branded terms.
For example, the following results (as of Oct. 2017) are showing when you type in united airlines into Google:
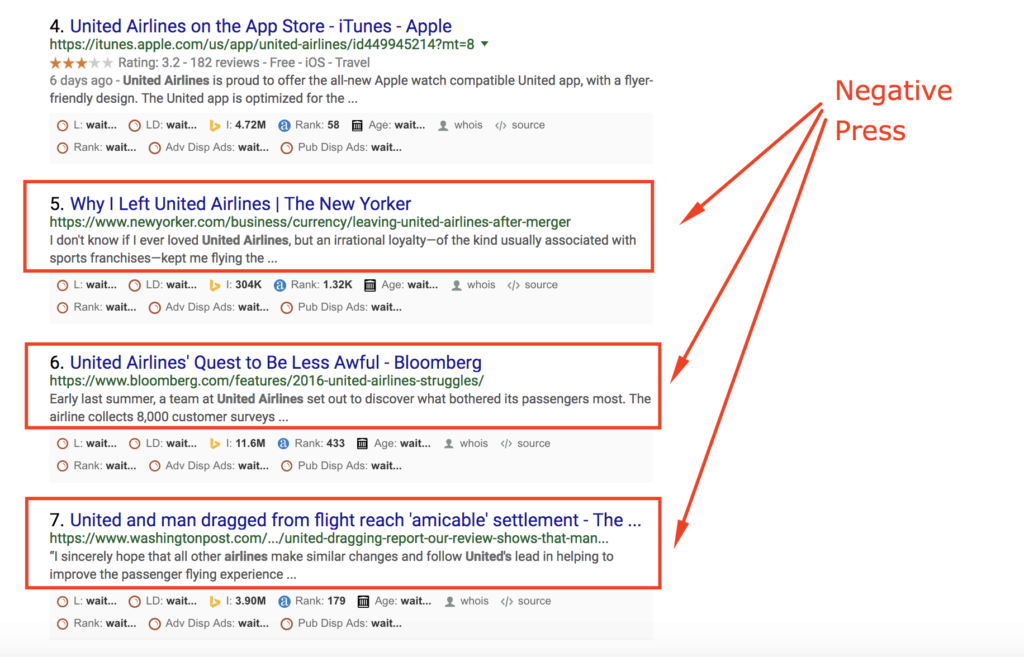 You see that results #5, #6, and #7 are all articles that are potentially harmful to United Airlines brand image if people were to read these.
You see that results #5, #6, and #7 are all articles that are potentially harmful to United Airlines brand image if people were to read these.
This company is probably not too happy about having negative press saturate the bottom half of the first page for their brand name.
That’s where reverse SEO comes in. You can work on boosting up other more positive results to suppress the negative results. In SEO, I view it as “the cream rises to the top” (assuming you don’t get spam penalties, then you get penalized). With reverse SEO, you are telling Google which pages are the cream that should be rising to the top.
You should always be prepared to do some reverse SEO if the need arises.
What they should do in this case
So to do some reverse SEO, they would want to do some white hat SEO to the more flattering search results, in an attempt to crowd out the negative press articles.
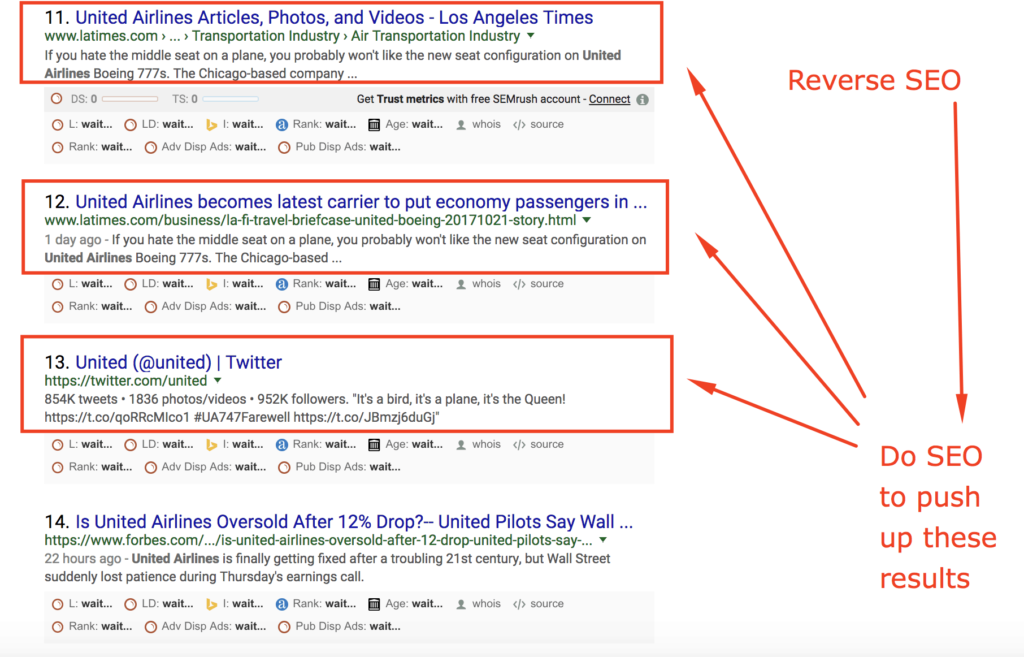
So if the results on the bottom of page 1 are articles that harm the brand’s image, you would want to do some reverse SEO. You are basically doing regular SEO on the results on the top page of 2, to enhance their rankings.
If you are able to rank a page 2 result higher, it will naturally push down one of those negative results. Remember, the cream rises to the top. When you push up a lower result, it displaces a higher result and the bad press article moves down.
Reverse SEO when the negative press goes viral.
If something happened to your company that harms your brand, and it went viral (ie. Many large websites picked it up), you may have a hard time doing reverse SEO.
The reason is that there will not only be a ton of sites talking about this negative aspect, but there will also be a lot of authority sites that are talking about the bad press.
These authority sites are naturally harder to push down through ranking other more positive articles because of their established authority makes it harder to outrank.
At that point, it may be a lost cause and may be better to just focus on other aspects of reputation management to rebuild your brand’s image.
Are you doing negative SEO on the pages you don’t want to be ranked?
What is negative SEO?
Negative SEO is where you intentionally do some spammy, or black hat SEO on a particular result in an attempt to sabotage it. You focus on the black hat tactics that Google has already caught onto and accounted for in their ago (i.e build thousands of article directory links).
The idea is that you are making it look like another site is engaging in black hat SEO, hoping they get a penalty, and thus get pushed down in the search results.
Negative SEO doesn’t work (apparently)
Normally, with reverse SEO, you wouldn’t use negative SEO. I suppose you could. However, I do NOT recommend negative SEO. You should never do negative SEO in the first place – it is immoral and is a waste of time anyways. Google is smart enough to know that it is negative SEO.
In fact, Gary Illyes has claimed that there has been no single case that negative SEO has ever worked. Post penguin 4.0, Google isn’t too concerned with Negative SEO, and I don’t think you should worry about it either:
 So does Negative SEO work? Honestly, I don’t know. I don’t think it does, but I have never engaged in any tactics like this.
So does Negative SEO work? Honestly, I don’t know. I don’t think it does, but I have never engaged in any tactics like this.
With that said, I’ve seen some definite cases of reverse SEO. One example was when I was looking at another site’s link profile. I could see that they had some anchor text attacks, (which were pretty funny). People were basically building links with spammy anchor text.
The result?
It appeared to do absolutely nothing. At the time I saw this spammed to death anchor text profile, this particular website was ranking #1 still in a very competitive niche.
So naturally, Google must have known that this was negative SEO. They do hire some of the smartest people in the world after all. They are capable of building software algorithms that can account for negative SEO.
Whether negative SEO works or not, the point is, doing white hat SEO and adding value is the best way to do reverse SEO.
 How to do Reverse SEO to help with your reputation management
How to do Reverse SEO to help with your reputation management
One of the best ways to have power and control over your reputation management is by owning the top 10 search results. Well, you don’t actually own it, but because you influence all the first page rankings, you essentially own those search results.
Reverse SEO Challenges
However, this requires ranking not just one site with SEO, it requires you rank 5-10 sites or more, depending on how many results you want to reverse.
Reverse SEO is very resource intensive and takes a lot of work. This is in large part because you don’t control the websites that you want to rank higher. You are trying to do SEO on sites you don’t own, which offers more of a challenge.
You can’t do on-page SEO.
With reverse SEO, you can’t do on-page SEO. You have to do SEO with purely off page tactics. This means link building.
And in 2017 link building is not easy. Or at the very least, it can be resource intensive.
Since off-page SEO is getting harder and harder to do, it will likely take a lot of work to do reverse SEO. This of course depends on the competitive landscape of the current ranking articles.
Steps to do Reverse SEO
Sites You Don’t Own: Promote articles to suppress the bad ones
- Set Goals: Target the negative press articles that you want to suppress (reverse SEO)
- Competitive Analysis: Do a competitive analysis on the articles that have the bad press against the articles that you want to displace these with (i.e find out how difficult it will be to outrank these vs the other more flattering or neutral articles)
- Build Links: Start by scraping the backlinks of the current ranking (negative press) sites. Then start doing some other form of white hat link building like guest posting or outreach.
- Rinse and Repeat: Repeat until you see results.
Sites You Do Own: On page and off page tactics to suppress the bad ones
- Set Goals: Again, target the negative press articles that you want to suppress using reverse SEO.
- Optimize Current Properties: If you already own certain websites, start by optimizing these if they are not ranking for your branded terms.
- Build New Web Properties: You can build out articles that target your brand keywords on Web 2.0 properties or other blogging platforms such as Medium. Really, anything with a high overall authority (you can look at Domain Authority) will help in your efforts to do reverse SEO.
- Competitive Analysis: Do a competitive analysis on the articles that have the bad press against the websites you do own.
- Build Links: Start by scraping the backlinks of the current ranking (negative press) sites. Then start doing some other form of white hat link building like guest posting or outreach.
- Internal linking: Since you do own the site, one thing you can do is use keyword rich internal linking.
- Rinse and Repeat: Repeat until you see results.

Jeffrey, your article touches a very interesting subject in SEO field. It make some points clearer for me. I’d have a question: when you mention “competitive analysis on the articles that have the bad press against the articles that you want to displace”, what would you say in case this article is from a major local paper (i.e. Washington Post) regarding a client’s local business in Washington? Any chance?
Hey there,
So it really doesn’t matter whether its a major local paper or national paper. It really just depends on how strong their authority is (i.e lots of links).
So when talking about doing competitive analysis, I am talking about doing some analysis to see how hard it is to outrank those articles. So looking at factors like DA, PA, TF, CF, Trust ratio, referring domains, age, etc. You can do this with many tools, but it is time-consuming if you want to do more than mozbar/ SEOquake extensions. I like the “keyword analyzer” in Serped as it allows me to fetch a lot of this data quickly. I even have a google sheets template that I use to further analyze it from the serped data. I’ll have to do a post on this.
So for example, let’s say the marketing team at United Airlines wanted to see how difficult it would be to outrank (or displace) washington post’s article. They could look at the DA, PA, Age, Referring domains, etc of their own site versus the Washington post page:
This is a screenshot of the “keyword analyzer” in Serped